In the ever-evolving world of mobile operating systems, Apple has consistently been at the forefront, setting the bar higher with each new release. One significant milestone in Apple’s iOS journey was the transition from iOS 6 to iOS 7. This shift marked a turning point in the design, features, and overall user experience of the iOS ecosystem.
In this blog post, we delve into the captivating realm of iOS 6 versus iOS 7, exploring the main differences between these two versions and shedding light on their unique characteristics. Whether you are an iOS enthusiast, a curious user, or someone contemplating an upgrade, this discussion will provide you with valuable insights into the evolution of Apple’s mobile operating sy
Get ready to embark on a journey through time and witness the transformative changes that iOS 6 and iOS 7 brought to the table. From the user interface to new features and performance enhancements, we leave no stone unturned in our exploration of these two remarkable iOS versions. So, let’s dive in and unravel the intriguing world of iOS 6 versus iOS 7.
Understanding iOS 6 and iOS 7
iOS 6, released in 2012, served as a significant precursor to the revolutionary iOS 7. Building upon the success of its predecessors, iOS 6 introduced a range of features and improvements that enhanced the overall user experience.
iOS 6 was hailed for its refined and polished interface, which retained the familiar grid-like home screen layout with app icons. It offered a seamless and intuitive user experience, allowing users to navigate through their devices effortlessly. Notable features included a revamped Siri with expanded capabilities, deeper integration with social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter, and enhancements to the already impressive camera app.
Additionally, iOS 6 introduced the much-anticipated Apple Maps, aiming to provide users with an alternative to third-party mapping services. While it showcased impressive 3D views and turn-by-turn navigation, it faced initial criticism for inaccuracies and missing information. However, Apple addressed these concerns through subsequent updates, gradually improving the accuracy and reliability of Apple Maps.
With the release of iOS 7 in 2013, Apple unveiled a radical redesign and a host of new features, ushering in a new era for its mobile operating system. The excitement and anticipation surrounding iOS 7 were palpable, as users eagerly awaited the arrival of a fresh and innovative experience.
iOS 7 marked a departure from the skeuomorphic design elements of its predecessors, embracing a flatter and more minimalist aesthetic. The interface underwent a complete transformation, featuring vibrant colors, translucent overlays, and simplified iconography. This visually stunning overhaul breathed new life into the iOS ecosystem, captivating users with its modern and dynamic appeal.
Beyond its visual enhancements, iOS 7 introduced numerous features that aimed to elevate the user experience. Control Center made its debut, offering quick access to commonly used settings and controls with a simple swipe. The multitasking interface was revamped, allowing users to effortlessly switch between apps and preview their content. Additionally, iOS 7 introduced AirDrop for seamless file sharing, improved notifications, and a redesigned App Store with enhanced discovery capabilities.
The release of iOS 7 sparked enthusiasm and set a new benchmark for mobile operating systems. Its bold design choices and feature-rich nature solidified its place as a major milestone in Apple’s iOS journey, leaving a lasting impact on users and shaping the direction of future iOS iterations.
As we delve deeper into the world of iOS 6 versus iOS 7, we unravel the intricate details that make each version unique. From the refined experience of iOS 6 to the revolutionary redesign of iOS 7, join us on this enlightening exploration of two remarkable chapters in Apple’s mobile operating system evolution.
User Interface: iOS 6 vs. iOS 7
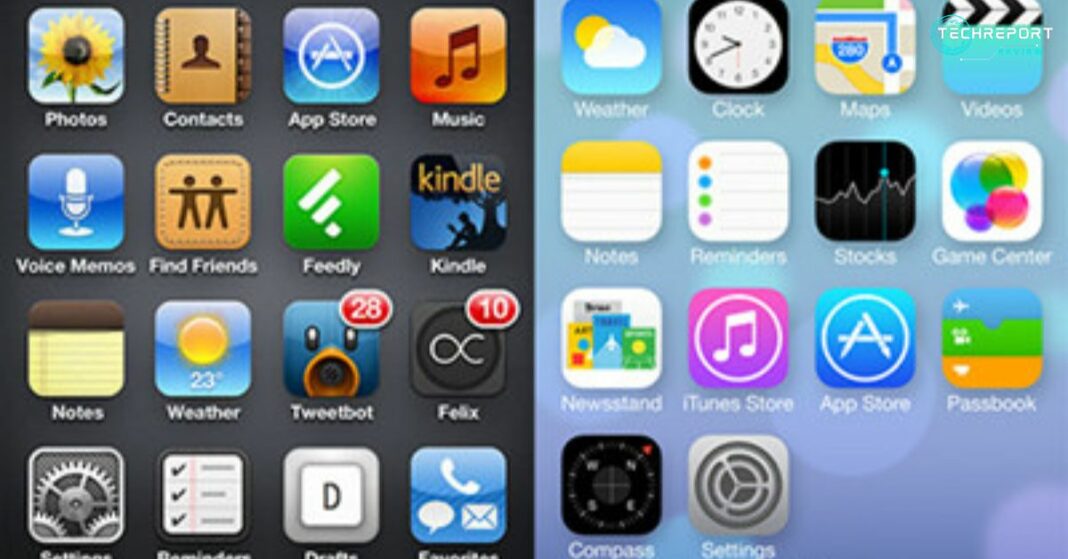
When it comes to the user interface, iOS 6 had a distinct visual design that relied on skeuomorphic elements. Released before the advent of iOS 7, it embraced a more realistic approach, mimicking real-world objects and textures. The interface featured iconic app icons that resembled their physical counterparts, complete with detailed textures and shadows. Users were greeted with a familiar grid-like home screen, adorned with app icons that represented various functionalities.
The overall aesthetic of iOS 6 exuded a sense of familiarity and comfort, with design elements reminiscent of traditional interfaces. The Notes app, for example, resembled a yellow notepad, complete with lined paper and a faux leather texture. Similarly, the Game Center app featured a felt-like background with a green baize texture, giving it the appearance of a gaming table.
iOS 7 marked a significant departure from the skeuomorphic design of its predecessor. It introduced a radical redesign, embracing a flat user interface approach that aimed for simplicity, clarity, and a modern look. The design language of iOS 7 focused on cleaner lines, bold colors, and a more minimalistic aesthetic.
Gone were the skeuomorphic textures and realistic icons of iOS 6. Instead, iOS 7 introduced a flatter design with icons that were simplified and more abstract. The icons were created using a grid system, with cleaner lines and reduced visual noise. The overall interface adopted a more vibrant color palette, with translucent overlays adding depth and a sense of visual hierarchy.
One of the notable additions in iOS 7 was the Control Center, accessible by swiping up from the bottom of the screen. This feature provided quick access to commonly used settings, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and screen brightness. It offered convenience and streamlined access to essential functions, eliminating the need to navigate through multiple settings menus.
iOS 7 also introduced significant updates to the Notification Center, which now included three tabs: Today, All, and Missed. The redesigned notification banners became more minimalistic and less obtrusive, allowing users to stay informed without interrupting their workflow.
Furthermore, iOS 7 featured a new multitasking interface, allowing users to preview app content in a card-like format by double-clicking the home button. This enhanced multitasking experience allowed for seamless app switching and provided users with a glimpse of their most recent interactions.
The user interface of iOS 7 represented a paradigm shift in Apple’s design philosophy. The flat UI approach brought a fresh, modern look to the iOS ecosystem, emphasizing simplicity and elegance. From the redesigned icons to the introduction of the Control Center and revamped Notification Center, iOS 7 provided users with a visually cohesive and streamlined interface that set the stage for future iterations of iOS.
Performance and Efficiency: iOS 6 vs. iOS 7
iOS 6 was known for its overall smooth performance on compatible devices. It offered a responsive and snappy user experience, with swift app launches and fluid animations. The operating system was optimized to run efficiently on devices of that era, ensuring a satisfactory performance for most users.
However, as with any software, iOS 6 did have its share of performance issues. Some users reported occasional lag or slowdowns, particularly on older devices or when running resource-intensive apps. These performance limitations were more evident on devices with limited RAM or slower processors. Additionally, as iOS 6 received updates and new features, some users found that their devices struggled to keep up with the increasing demands, resulting in decreased performance.
iOS 7 introduced several performance improvements and optimizations aimed at enhancing the overall user experience. Apple focused on making the operating system faster, more efficient, and better equipped to handle the demands of modern apps and features.
One of the significant improvements in iOS 7 was the introduction of a more advanced graphics system, which leveraged the capabilities of the device’s GPU to deliver smoother animations and transitions. This optimization resulted in a more fluid and responsive interface, contributing to an overall perception of improved speed.
Furthermore, iOS 7 implemented background app refresh, a feature that allowed apps to update their content in the background while preserving battery life and performance. This change reduced the strain on system resources and ensured that apps were up-to-date and ready for use when launched.
In terms of efficiency, iOS 7 aimed to optimize power consumption, prolong battery life, and improve the overall device performance. The operating system introduced features like automatic app updates, which minimized the need for manual updates and reduced battery drain caused by multiple app refreshes.
iOS 7 also implemented smarter scheduling of system tasks and improved memory management. These enhancements helped allocate system resources more efficiently, resulting in better performance and reduced lag.
Overall, iOS 7 brought noticeable improvements to the performance and efficiency of compatible devices. Users experienced smoother animations, faster app launches, and better overall system responsiveness. The optimizations made in iOS 7 aimed to provide a better user experience while maintaining a balance between performance and battery life.
While iOS 7 was generally considered faster and more efficient than iOS 6, the actual performance experienced by users could vary depending on the specific device model and hardware capabilities. Newer devices tended to benefit more from the optimizations, while older devices may still experience some performance limitations due to hardware constraints.
It is important to note that as iOS versions progressed beyond iOS 7, subsequent updates and features were tailored to newer devices, which may have impacted the overall performance of older devices running iOS 7.
Upgrading from iOS 6 to iOS 7
The Upgrade Process
Upgrading from iOS 6 to iOS 7 is a relatively straightforward process. Follow these step-by-step instructions to ensure a smooth transition:
- Check Device Compatibility: Before proceeding with the upgrade, verify that your device is compatible with iOS 7. Apple typically provides a list of compatible devices on its website. Keep in mind that some older devices may not support iOS 7 due to hardware limitations.
- Backup Your Device: Before making any changes to your device’s operating system, it is crucial to back up your data. This can be done through iCloud or by connecting your device to a computer and using iTunes. By creating a backup, you can safeguard your personal information and ensure a seamless restoration if any issues arise during the upgrade process.
- Connect to a Stable Network: Ensure that your device is connected to a stable and reliable Wi-Fi network. Upgrading to iOS 7 requires a substantial amount of data, and a stable internet connection will prevent interruptions during the download and installation process.
- Start the Upgrade: Once you have completed the above steps, navigate to the Settings app on your device. Tap on “General” and then select “Software Update.” If an update is available, you will see the option to download and install iOS 7. Follow the on-screen prompts to initiate the upgrade.
- Installation and Setup: The upgrade process will involve downloading the iOS 7 software package to your device. Once the download is complete, the installation will begin automatically. Your device may restart several times during the installation process, so be patient and avoid interrupting the process.
- Configure iOS 7: After the installation is complete, your device will restart and prompt you to configure iOS 7. Follow the on-screen instructions to set up your device preferences, including Wi-Fi networks, Apple ID, and iCloud settings.
Advantages of Upgrading
Upgrading to iOS 7 brings several advantages and new features to enhance your overall user experience:
- Fresh and Modern Design: iOS 7 introduced a visually appealing and modern design language, offering a significant departure from the skeuomorphic design elements of iOS 6. The interface became cleaner, flatter, and more vibrant, providing a more contemporary look and feel.
- Enhanced Multitasking: iOS 7 introduced improved multitasking capabilities, allowing users to easily switch between recently used apps. The new multitasking view displayed app previews, making it easier to navigate and manage multiple tasks simultaneously.
- Control Center: iOS 7 introduced the Control Center, a convenient feature accessible by swiping up from the bottom of the screen. The Control Center provides quick access to commonly used settings such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, screen brightness, and music playback controls.
- Notification Center: iOS 7 revamped the Notification Center, providing a cleaner and more organized interface. Notifications were categorized into “Today,” “All,” and “Missed” sections, making it easier to manage and prioritize incoming notifications.
- Siri Enhancements: With iOS 7, Siri received several improvements, including a refined voice and the ability to access settings like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and brightness controls. Siri also gained the ability to provide more accurate search results and integrate with additional apps.
- AirDrop: iOS 7 introduced AirDrop, a feature that allows users to share files wirelessly with nearby devices. With AirDrop, users can easily share photos, videos, contacts, and other supported files with a simple tap.
- App Store Updates: Upgrading to iOS 7 provides access to the latest versions of apps available in the App Store. Many app developers started optimizing their apps specifically for iOS 7, taking advantage of its new features and design elements.
Sticking with iOS 6
While upgrading to iOS 7 offers numerous benefits, some users may have reasons to stick with iOS 6:
- Device Compatibility: As mentioned earlier, not all older devices are compatible with iOS 7. If you have an older device that is not supported, you will not have the option to upgrade. In such cases, sticking with iOS 6 may be the only choice.
- Familiarity and Skeuomorphic Design: iOS 6 had a distinct skeuomorphic design that some users found familiar and comfortable. If you prefer the visual aesthetics and design elements of iOS 6, you may choose to stay with the older version.
- Performance on Older Devices: While iOS 7 introduced performance improvements, some older devices may struggle to handle the demands of the new operating system. If you have an older device with limited resources, staying on iOS 6 may provide a smoother performance.
- App Compatibility: Although many app developers updated their apps for iOS 7, some older apps may not be fully optimized or compatible with the newer operating system. If you heavily rely on specific apps that have not been updated for iOS 7, staying on iOS 6 may be preferable to maintain app compatibility.
It is essential to weigh the advantages and considerations before making a decision. Upgrading to iOS 7 offers a refreshed user interface, new features, and improved performance. However, sticking with iOS 6 may provide familiarity and compatibility benefits, particularly on older devices. Ultimately, the choice between iOS 6 and iOS 7 depends on your specific device, preferences, and individual needs.
Compatibility and App Ecosystem
Compatibility with iOS 6
- iOS 6 Compatibility: iOS 6 was designed to run on a range of Apple devices, including iPhones, iPads, and iPod touch. It supported several older devices, including the iPhone 3GS, iPhone 4, and fourth-generation iPod touch. Additionally, it was compatible with the iPad 2 and third-generation iPad.
- Supported Apps: iOS 6 offered compatibility with a wide range of apps available in the App Store at that time. Many popular apps and services were designed to work seamlessly on iOS 6, providing users with access to various functionalities such as social media, productivity tools, games, and entertainment apps.
However, as iOS versions advance, app developers tend to optimize their apps for the latest operating systems. As a result, some newer apps and features may need to be available or fully supported on iOS 6. Users may experience limitations when it comes to accessing the latest app updates, features, and security enhancements. It’s essential to consider these factors when deciding whether to stick with iOS 6 or upgrade to iOS 7.
Compatibility with iOS 7
- Expanded Device Compatibility: iOS 7 introduced expanded device compatibility compared to iOS 6. It supported newer devices such as the iPhone 5, iPhone 5S, iPhone 5C, iPad 4th generation, and the iPad Mini. With this wider range of supported devices, more users had the opportunity to upgrade to iOS 7 and experience its new features.
- Support for Newer Apps: Upgrading to iOS 7 provided users with access to the latest versions of apps available in the App Store. App developers are increasingly focused on optimizing their apps for iOS 7’s new design language, features, and APIs. This meant that newer apps and app updates were more likely to be compatible and fully functional on iOS 7.
However, it’s important to consider the potential incompatibilities that may arise when upgrading older devices to iOS 7. While some older devices were compatible with iOS 7, their hardware specifications might limit certain functionalities or result in slower performance compared to newer devices. Users with older devices should evaluate whether the potential performance trade-offs are acceptable before deciding to upgrade to iOS 7.
When considering compatibility and the app ecosystem, it’s advisable to check the system requirements of specific apps you rely on or plan to use. Some apps may require a minimum iOS version beyond iOS 6 to run optimally or access the latest features. Assessing your device’s compatibility and the availability of app updates for your desired apps can help inform your decision between sticking with iOS 6 or upgrading to iOS 7.
Security Features: iOS 6 vs. iOS 7
Security in iOS 6
- Security Features: iOS 6 implemented several security measures to safeguard user data and protect against potential threats. These included data protection, secure boot chain, code signing, and sandboxing. Data protection ensured that files stored on the device were encrypted and inaccessible without the device passcode. Secure boot chain ensured the integrity of the operating system during startup, preventing unauthorized modifications. Code signing verified the authenticity of apps before allowing them to run, reducing the risk of malicious software. Sandboxing restricted the access and actions of apps, preventing them from accessing sensitive user information or interfering with other apps.
- User Protection: iOS 6 aimed to provide a secure environment for users by prioritizing privacy and data protection. Users had control over app permissions, allowing them to grant or deny access to personal information such as location data, contacts, and photos. Additionally, iOS 6 included a Find My iPhone feature that allowed users to remotely locate, lock, or erase their devices if lost or stolen.
Security in iOS 7
- Enhanced Security Features: With the release of iOS 7, Apple introduced several enhancements to further strengthen the security of the operating system. One notable addition was the Activation Lock feature, which required users to enter their Apple ID and password to activate a device, even after a remote erase. This feature made stolen devices less valuable as they couldn’t be reactivated without the original owner’s credentials. iOS 7 also introduced a strengthened data protection mechanism, extending encryption to more areas of the device, including email attachments and third-party apps that adopted the feature.
- Addressing Vulnerabilities: iOS 7 addressed potential vulnerabilities and security weaknesses present in previous versions. It included security patches and fixes for known issues, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or exploitation of system vulnerabilities. Apple actively monitored and responded to security threats, releasing regular updates and security patches to protect users.
Furthermore, iOS 7 introduced app-specific passwords for accessing iCloud services, providing an additional layer of security for users who wanted to grant access to their iCloud data while keeping their primary Apple ID password confidential.
Overall, iOS 7 offered enhanced security features and improvements compared to iOS 6. It aimed to provide users with a robust and secure environment, protecting their data, privacy, and device integrity. Apple’s continued focus on security and proactive response to emerging threats helped maintain the reputation of iOS as a secure mobile operating system.
Bug Fixes and Known Issues
Bugs and Issues in iOS 6
- Known Bugs: Like any software, iOS 6 had its share of bugs and issues that affected user experience. Some of the notable bugs included occasional Wi-Fi connectivity problems, battery drain issues, and occasional app crashes or freezes. Additionally, users reported occasional issues with Siri, the voice assistant feature, not functioning as expected in certain scenarios.
- Fixes and Improvements in iOS 7: When Apple released iOS 7, they aimed to address many of the bugs and issues present in iOS 6. Through updates and patches, Apple sought to provide a more stable and reliable operating system. Some of the significant fixes and improvements included enhanced Wi-Fi connectivity, improved battery management algorithms, and overall system stability enhancements. Furthermore, Apple made efforts to refine the performance of Siri and address any reported issues to ensure a smoother user experience.
Bugs and Issues in iOS 7
- Reported Bugs and Issues: Despite Apple’s efforts, iOS 7 also faced its share of reported bugs and issues upon release. Users reported issues related to app compatibility, occasional crashes, and minor graphical glitches. Some users also experienced problems with Bluetooth connectivity or encountered issues with certain features not working consistently across all devices.
- Apple’s Response: Apple actively monitored user feedback and bug reports to identify and address the reported issues. They released regular updates and patches to address the bugs and provide fixes for the reported issues. Through these updates, Apple aimed to improve system stability, resolve compatibility problems, and enhance the overall user experience. They encouraged users to report any issues they encountered, enabling Apple to gather data and insights for further bug fixes and improvements.
Apple’s commitment to addressing bugs and issues demonstrated its dedication to providing a reliable and user-friendly operating system. The regular updates and bug fixes aimed to ensure that users could enjoy a smooth and hassle-free experience with their iOS devices. While no software is entirely bug-free, Apple’s proactive approach to resolving issues helped maintain the performance and reliability of iOS 7.
Storage Space Requirements: iOS 6 vs. iOS 7
Storage Space in iOS 6
- Storage Space Required: iOS 6, being an earlier version of the operating system, had relatively lower storage space requirements compared to its successor, iOS 7. The exact amount of storage space required by iOS 6 varied depending on the device and the specific version of the operating system. On average, iOS 6 typically occupied around 1.5 to 2.0 gigabytes (GB) of storage space on compatible devices.
- Limitations and Considerations: While the storage space required by iOS 6 was relatively modest, it was still a consideration for users with devices that had limited storage capacity. Devices with lower storage options, such as 8 or 16 GB models, could potentially face storage constraints when installing and updating apps, downloading media files, or capturing photos and videos. Users had to be mindful of their available storage space and manage it efficiently to avoid running out of storage or experiencing performance issues.
Storage Space in iOS 7
- Increased Storage Requirements: With the release of iOS 7, the storage space requirements increased compared to iOS 6. The exact amount of storage space required by iOS 7 varied depending on the device model and the version of iOS 7. On average, iOS 7 occupied around 3.5 to 4.0 GB of storage space, nearly double that of iOS 6.
- Managing Storage on iOS 7 Devices: The increased storage requirements in iOS 7 meant that users with devices with limited storage capacity needed to be more cautious about their storage usage. To manage storage on iOS 7 devices effectively, users could employ various strategies:
- Offloading Unused Apps: Users could offload or delete apps that were rarely used or no longer needed to free up storage space.
- Optimizing Media Files: Users could optimize their media files by using efficient compression techniques or by storing them in cloud storage services, reducing the local storage footprint.
- Clearing Cache and Temporary Files: Clearing cache and temporary files accumulated by apps could help reclaim storage space.
- Transferring Files to External Storage: Users could transfer files, such as photos and videos, to external storage devices or cloud-based services to free up space on their iOS 7 devices.
- Utilizing Storage Optimization Features: iOS 7 introduced storage optimization features, such as the option to automatically offload unused apps or to review and delete large attachments in Messages, which could assist in managing storage efficiently.
By employing these storage management strategies, users could effectively navigate the increased storage requirements in iOS 7 and ensure they had sufficient space for their apps, media, and other content without compromising device performance or usability.
User Experience: iOS 6 vs. iOS 7
User Experience in iOS 6
- Overall User Experience: iOS 6 provided users with a familiar and stable user experience. It offered a refined interface, smooth navigation, and a range of features that were well-received by users. The user experience in iOS 6 was characterized by its skeuomorphic design, with realistic textures, icons, and visual elements that resembled their real-world counterparts. The interface was intuitive and easy to navigate, with a focus on simplicity and accessibility.
- User Feedback: Overall, iOS 6 received positive feedback from users. Many appreciated its ease of use, familiar design, and seamless integration with other Apple devices and services. Users praised the stability and reliability of the operating system, as well as its extensive app ecosystem, which offered a wide range of high-quality applications.
User Experience in iOS 7
- User Experience Improvements: iOS 7 brought significant changes to the user experience, introducing a fresh and modern design language. The flat user interface replaced the skeuomorphic design of iOS 6, embracing a simpler and more minimalist aesthetic. The interface featured vibrant colors, clean typography, and a focus on content. iOS 7 also introduced new gestures and animations that enhanced the overall fluidity and interactivity of the user experience.
- Reception and Feedback: The reception of iOS 7 among users was mixed. While many appreciated the new design direction and the added features, some users found the radical changes challenging to adapt to initially. The flat design, although visually appealing to some, received criticism from those who preferred the more textured and realistic visuals of iOS 6. Additionally, there were reports of performance issues and bugs in the initial release of iOS 7, which affected the overall user experience for some users.
However, over time, Apple addressed these issues through software updates, improving the performance and stability of iOS 7. As users became more accustomed to the redesigned interface and took advantage of the new features, the reception gradually became more positive.
The user experience in iOS 7 offered a fresh and modern feel, with improved multitasking, an enhanced notification center, and a revamped control center for quick access to commonly used settings. Despite the initial mixed reception, iOS 7 laid the foundation for future updates and paved the way for the evolution of Apple’s mobile operating system.
Overall, the user experience in iOS 6 and iOS 7 differed significantly due to the contrasting design languages and interface changes. While iOS 6 offered a familiar and refined experience, iOS 7 introduced a more modern and visually impactful interface that aimed to keep up with evolving design trends.
Battery Life: iOS 6 vs. iOS 7
Battery Life in iOS 6
- Battery Life Performance: iOS 6 was known for its efficient battery management on compatible devices. Users generally experienced satisfactory battery life during regular usage, including web browsing, app usage, and multimedia consumption. The operating system implemented power-saving techniques and optimizations to ensure a balance between performance and battery consumption.
- Known Issues and Considerations: While iOS 6 generally offered good battery life, some users reported specific issues or considerations. For example, heavy usage of power-intensive features such as GPS navigation or video streaming could result in faster battery drain. Additionally, certain background processes or poorly optimized third-party apps could also contribute to increased battery consumption. However, these issues were typically isolated and did not affect the majority of users.
Battery Life in iOS 7
- Battery Life Improvements: iOS 7 introduced various optimizations and enhancements aimed at improving battery life. Apple focused on reducing unnecessary background activity, optimizing system resources, and implementing power-saving technologies. These efforts were designed to maximize battery efficiency and ensure a longer-lasting battery life on compatible devices.
- Battery Management in iOS 7: iOS 7 implemented several features to better manage battery life. It included a Battery Usage section in the Settings app, allowing users to monitor and identify apps or processes that consumed significant battery power. This feature helped users identify and address potential battery-draining culprits. Furthermore, iOS 7 introduced background app refresh, which allowed users to control which apps can update in the background, thereby reducing unnecessary battery usage.
iOS 7 also improved power management during various activities. For example, it intelligently adjusted screen brightness based on ambient lighting conditions, reducing power consumption without compromising visibility. Additionally, iOS 7 introduced a low-power mode called “Battery Saver” (later renamed “Low Power Mode” in subsequent iOS versions), which temporarily disabled non-essential features to extend battery life when the device’s charge dropped to a certain level.
Overall, iOS 7 demonstrated a commitment to improving battery life by implementing optimizations, providing user visibility into battery usage, and introducing features to conserve power. While individual experiences may vary based on device usage patterns and settings, iOS 7 generally offered a comparable or improved battery life compared to iOS 6.
It’s worth noting that Apple continued to refine battery life management in subsequent iOS updates, addressing any potential issues or further optimizing power consumption. Users were encouraged to keep their devices updated with the latest iOS version to benefit from ongoing battery life improvements.
Downgrading from iOS 7 to iOS 6
The Downgrade Process
Downgrading from iOS 7 to iOS 6 is a process that requires careful consideration and preparation. While Apple does not officially support downgrading, it may be possible to revert to iOS 6 under certain circumstances. However, it’s important to note that the availability and success of downgrading methods may vary depending on device models and specific iOS versions.
To downgrade from iOS 7 to iOS 6, users typically need to follow a series of steps that involve downloading the iOS 6 firmware file, putting the device into DFU (Device Firmware Update) mode, and using iTunes to restore the device using the iOS 6 firmware. It’s crucial to back up all data before attempting a downgrade, as the process erases all content and settings on the device.
It’s essential to understand that downgrading to iOS 6 from iOS 7 is not officially supported by Apple. As a result, there are limitations and potential risks associated with the process. These may include:
- Compatibility Issues: Downgrading to iOS 6 may not be possible on certain newer devices that lack firmware compatibility with iOS 6. Users should check the availability of iOS 6 for their specific device model before attempting a downgrade.
- App Support and Compatibility: iOS 6 is an older operating system, and some apps may no longer be compatible or receive updates for this version. Users should be prepared for potential app compatibility issues, limited feature sets, or missing functionality when using iOS 6.
- Security Considerations: Downgrading to an older iOS version means missing out on the latest security updates and patches provided by Apple. This can potentially expose the device to known security vulnerabilities present in earlier versions of iOS.
Reverting to iOS 6
Reasons for Downgrading: Users may have various reasons for considering a downgrade from iOS 7 to iOS 6. Some common motivations include:
- Preference for iOS 6’s Design: iOS 7 introduced a significant visual overhaul, adopting a flatter and more modern design language. However, some users may have a personal preference for the skeuomorphic design elements and overall aesthetics of iOS 6.
- App Compatibility: As mentioned earlier, certain older apps may not receive updates for iOS 7 or newer versions, making them incompatible or limited in functionality. Users who heavily rely on specific apps that are optimized for iOS 6 may choose to downgrade to ensure full app compatibility.
- Performance on Older Devices: While iOS 7 aimed to provide a better user experience, some users with older devices might have experienced performance issues or decreased responsiveness after upgrading. Downgrading to iOS 6 may alleviate these concerns and offer a smoother experience on aging hardware.
Reverting to iOS 6 after using iOS 7 involves transitioning back to an older operating system with its own set of features, limitations, and design choices. Users should be prepared for a different user experience and potential adjustments when using iOS 6.
It’s important to note that downgrading to iOS 6 is not a recommended or officially supported solution. Apple encourages users to stay up-to-date with the latest iOS version, as each update includes important security patches, bug fixes, and performance improvements. If users encounter issues or concerns with iOS 7 or newer versions, they should consider alternative solutions such as troubleshooting, optimizing settings, or seeking assistance from Apple support channels before considering a downgrade.
In Crux
In this comparison between iOS 6 and iOS 7, we have explored the key differences, features, and user experiences offered by both versions of Apple’s mobile operating system. Each version brought significant changes and enhancements to the iOS ecosystem, catering to different user preferences and needs. Let’s summarize the main points discussed and offer some personal insights and recommendations based on the comparison.
iOS 6, released as the predecessor to iOS 7, introduced notable features and improvements of its own. With its skeuomorphic design elements and familiar user interface, iOS 6 provided a visually pleasing and intuitive experience. It offered features such as Siri integration, a comprehensive app ecosystem, and stable performance on compatible devices. iOS 6 appealed to users who preferred a more traditional design approach and relied heavily on certain apps optimized for this version.
On the other hand, iOS 7 marked a significant shift in Apple’s design language and introduced a more modern, flat UI approach. The redesigned interface, cleaner aesthetics, and updated icons brought a fresh and contemporary feel to the operating system. iOS 7 also introduced features like the Control Center, Notification Center, and enhanced multitasking capabilities, aiming to provide a more streamlined and efficient user experience.
When it comes to performance and efficiency, both iOS 6 and iOS 7 have their strengths and weaknesses. iOS 6 showcased stability and smoothness on compatible devices, while iOS 7 introduced performance improvements and optimizations. However, it’s worth noting that older devices may experience slower performance on iOS 7 due to the increased demands of the new features and design elements.
The upgrade process from iOS 6 to iOS 7 was straightforward, but users should carefully consider their device’s compatibility and potential limitations before making the switch. Upgrading to iOS 7 offered various benefits, including access to the latest features, improved user experience, and compatibility with newer apps and services. However, some users might prefer to stick with iOS 6 due to personal preferences, app compatibility concerns, or a desire to maintain familiarity with the previous version.
In terms of security, both iOS 6 and iOS 7 provided measures to protect user data and ensure device security. However, iOS 7 introduced enhanced security features and addressed potential vulnerabilities more comprehensively. Therefore, from a security standpoint, iOS 7 is recommended for users who prioritize the latest security updates and patches.
It’s important to consider the app ecosystem when deciding between iOS 6 and iOS 7. While iOS 6 boasts a vast collection of apps compatible with older devices, app developers have shifted their focus to optimizing their offerings for newer iOS versions. Users relying heavily on specific apps should take this into account when making their decision.
Battery life is a crucial factor for many users. Both iOS 6 and iOS 7 had their respective impacts on battery consumption. While iOS 7 introduced optimizations to improve battery life, the newer features and design elements could still affect overall battery performance. Users should be mindful of their usage patterns and preferences when considering the impact on battery life.
Lastly, readers need to make an informed decision based on their specific needs and preferences. Consider the design aesthetics, features, performance, app compatibility, security, and battery life considerations discussed in this comparison. Reflect on your usage habits, device compatibility, and desired user experience to determine which version suits you best.
In conclusion, iOS 6 and iOS 7 offered distinct experiences and features that catered to different user preferences and needs. Whether you appreciate the familiarity and traditional design of iOS 6 or prefer the modern and streamlined approach of iOS 7, the choice ultimately depends on your requirements. We encourage you to consider all aspects discussed in this comparison and make an informed decision that aligns with your specific needs and preferences.
Remember, both iOS 6 and iOS 7 have their own merits and considerations, and Apple continues to release newer versions with further improvements. It’s always a good practice to stay up-to-date with the latest iOS version, as it ensures access to the latest features, security updates, and app compatibility.
How much did you like our detailed iOS 6 vs iOS 7: A Journey Through Apple’s Mobile Revolution? Also, please share these Blogs with your friends on social media.
Related Blogs
- Is iPhone 14 Worth the Hype
- Unblock Banned Apps
- Best Cheap VPN Services
- Antenna vs Cable TV
- TiVo or DVR
- DLP vs LCOS
[WPSM_AC id=1180]